
Continue with
Registration Number
Continue without
Registration Number
I Have
Brand new Car
The total number of Indian taxpayers increased by over 80% in 9 years, and nearly 8.6 crore ITR or income tax returns were filed in the assessment year 2024-25. As our country moves from being a developing economy towards the status of an economic powerhouse, more and more citizens are likely to pay income tax.
The overall process of paying income tax has been simplified to a great extent, thanks to growing awareness and government initiatives, including the e-filing of income tax. That being said, there seems to be a lack of clarity on how to file an income tax return online.
Let's dig deep to define an ITR, find out who must file an income tax return, understand how to file an IT return online, and review the necessary documentation.
ITR expands to 'income tax return.' It is an authorized form, a mandatory filing for taxpayers, that reports one's income, expenses, investments and tax liabilities for the last financial year. The ITR form should be submitted to the Government of India's Income Tax Department.
Filing ITR is compulsory for all individuals and businesses whose gross income crosses the basic exemption limit, which may vary depending on your choice between the old and new tax regimes. ITR filing is also necessary in the following circumstances:
Benefits of Filing ITR Online?
Instructions on how to file an income tax return online step-by-step include the following steps:
Step 1: Visit the Government of India's e-filing portal and Log in using your PAN/Aadhaar or net banking credentials.

Step 2: Click 'e-File' on the top menu and choose 'Income Tax Returns.' And select 'File Income Tax Return' from the dropdown menu.

Step 3: and pick the correct 'Assessment Year' and Choose 'Online' as the 'Mode of Filing.'

Step 4: Select the right 'status applicable to you.'
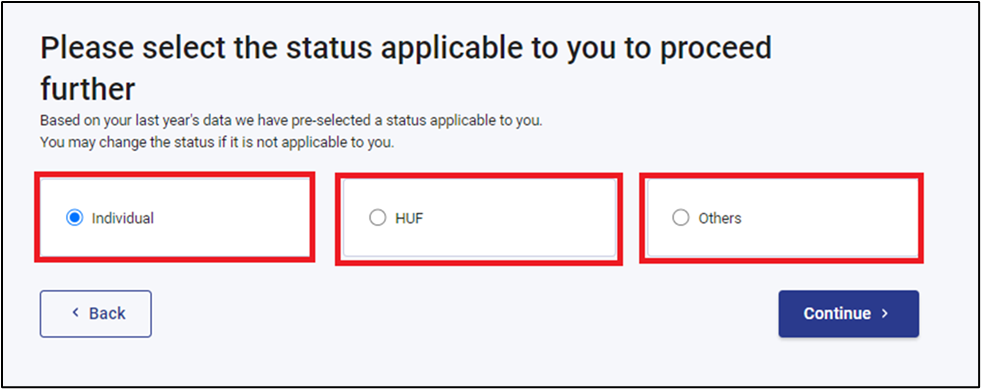
Step 5: Choose the 'ITR Form to proceed.'
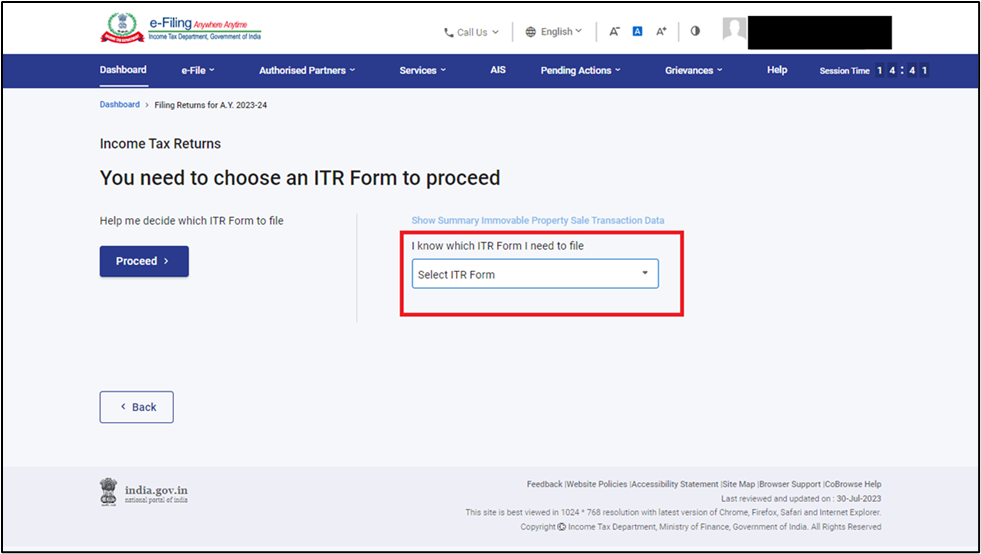
Step 6: Specify (select) 1/3 reasons for filing your returns.

Step 7: Carefully read/disclose your personal information, gross total income and deductions.
Step 8: Validate, confirm, verify, and submit your prefilled return summary.
DO NOT forget to E-Verify the return within 30 days by generating your EVC or 'Electronic Verification Code', using Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or sending a hard copy of ITR-V to the Income Tax Department's CPC in Bengaluru. Failing to do so could make your tax return invalid or null and void.
The income tax department digitally sends your ITR-V or 'Income Tax Return-Verification' form via email. That said, you may also download a copy. One must keep PAN and ITR-V acknowledgement numbers ready before taking the following steps:
Step 1: Log in to the Government of India's e-filing portal.
Step 2: Click 'e-File' on the top menu.
Step 3: Choose 'Income Tax Returns.'
Step 4: Select 'View Filed Returns' and pick the 'Assessment Year.'
Step 5: Finally, click on 'Download Form' and save it.
The CBDT, or 'Central Board of Direct Taxes', issues 7 ITR forms for specific categories, purposes and criteria. Below are their prominent applicability and non-applicability details:
Resident individual with a total yearly income of up to INR 50 lakh, including incomes from a salary/pension, one house property, an agricultural domain (maximum INR 5 thousand), long-term capital gains (not exceeding INR 1.25 lakh) and other sources.
*Not Applicable:
An HUF, 'Hindu Undivided Family', or an individual with income from salary/pension, house properties, agricultural domain exceeding INR 5 thousand, capital gains, foreign or other sources. This form is also to be utilized by individual directors in companies, resident not ordinarily residents (RNOR), non-residents, those who own assets outside India and whose tax has been deducted under Section 194N of the Income Tax Act.
*Not Applicable:
An individual or a 'Hindu Undivided Family' with income from proprietary businesses or professions, involved in maintaining accounts and/or getting them audited, and earns income as a firm partner.
*Not Applicable:
Resident individuals, HUFs and partnership firms (excluding LLPs) with total income not exceeding INR 50 lakh, including professional/business incomes, salaries, pensions, incomes from a one-house property, other sources and capital gains not crossing the INR 1.25 lakh mark.
*Not Applicable:
Covers BOIs or 'Body of Individuals', AOPs or 'Association of Persons', AJPs or 'Artificial Juridical Persons', LLPs or 'Limited Liability Partnerships', business trust plus investment funds, estates of deceased and insolvents.
*Not Applicable:
All companies registered under the Companies Act 2013 or the Companies Act 1956.
*Not Applicable:
Persons and companies who need to furnish returns under Section 139 (4A, 4B, 4C or 4D), religious/charitable trusts, political parties, news agencies, colleges/universities and scientific research associations.
*Not Applicable:
E-filing of income tax returns or ITRs can by all means be described as a pretty straightforward process that ensures timely compliance, precise factual reporting, faster processing, strengthens your financial stability and brings invaluable peace of mind.
While it is essential to declare your life or medical insurance policies when filing returns, picking the right one for your unique needs is equally important. And that's where QuickInsure comes in handy!
Reach out to the country's most admired insurance comparison portal, scan policies from all major service providers, study their features/benefits, evaluate pricing models, and close the purchase on your terms.
Barring some complex scenarios, yes, you certainly can! The easy-to-use and self-explanatory e-filing portal requires no assistance from CAs or professional financial experts.
When it comes to the financial year 2024-25, the last date for filing ITR is 31st July'25. Sometimes, the government authorities may extend the due date or deadline. However, if you missed the due date, you can file a belated return with late fees, penalties or interest by 31st December.
It's human to make mistakes! As per Section 139(5), you may rectify errors or omissions, and file a revised 'updated return' by 31st December of the assessment year or before assessment completion, whichever comes earlier. At least 60% of the aggregate tax and interest will be payable if the updated return is filed after the expiry of 24 months from the end of the relevant assessment year.
Income tax computation requires sufficient knowledge of taxation laws and all the latest Income Tax Act provisions/rules. Your income tax is calculated based on the information shared about income, expenses, investments, and deductions. It may include figures pertaining to your salary before deducting exemptions, taxable salary, interest/rental income, interest on home loan, other expenses, and tax-saving investments.
Estimating your taxes before filing is a wise step. However, unless absolutely sure, hiring a qualified tax consultant or relying upon a credible online tax calculator as a cost-effective alternative is advisable.
Note: The above information is purely indicative in nature and subject to change without any prior notice from the government authorities. One must refer to the Government of India's Income Tax Department portals to learn the most up-to-date developments before taking action.